Together for Forests
REDD+ Project
Healthy Forests, Thriving Communities
The project
Madre de Dios
260,000 ha of Amazon rainforest in Peru’s biodiversity capital
The Together for Forests REDD+ Project safeguards over 260,000 hectares of tropical Amazon forest in Peru’s Madre de Dios region — known as the country’s “biodiversity capital” and one of the most biologically rich places on Earth. This globally recognised biodiversity hotspot provides habitat for hundreds of rare and endangered species, from jaguars and tapirs to caimans and the world’s greatest concentration of bird species. It is also home to nearly 190,000 people, including 37 Indigenous communities, some living in voluntary isolation.
In recent decades, these forests have faced intense pressure from the expansion of the Inter‑Oceanic Highway, illegal mining, illegal logging, and the conversion of land to agriculture. In response, small forest concession holders and small‑scale forest owners — united through the Cooperative of Forest Owners of Madre de Dios (COOPAFSAMAD) — have committed to protecting this critical carbon sink. By combining local stewardship with sustainable forest management, the project aims to conserve biodiversity, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and create lasting benefits for the people who depend on the forest for their livelihoods.



STANDARD
Verra VCS
PROTOCOL
VM0048
CREDITS
VCUs
START YEAR
2024
VOLUMES EXPECTED
1Q 2026
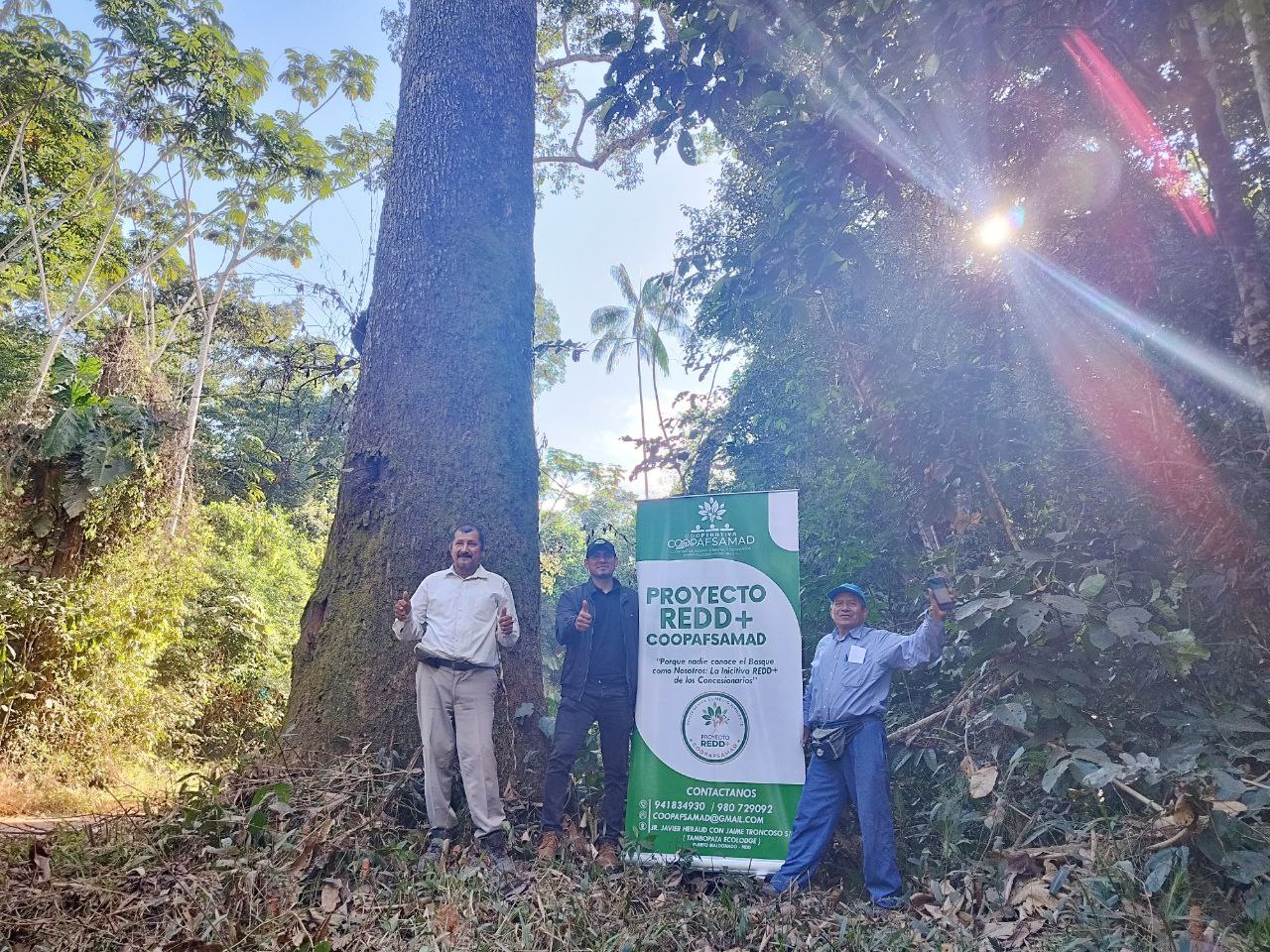



Activities
The project works to halt deforestation and forest degradation by strengthening governance across the cooperative and equipping members with the tools, knowledge, and technical capacity to manage their forests sustainably. Central to this approach is the development of an integrated monitoring system to track forest cover, biodiversity, and land use changes.
Improved forest management practices reduce the risk of illegal activity while sustaining timber and non‑timber forest production in line with environmental safeguards. Agroforestry systems are promoted on agricultural land to restore degraded areas and provide viable alternatives to destructive practices — improving food security, diversifying incomes, and reducing pressure on standing forest.
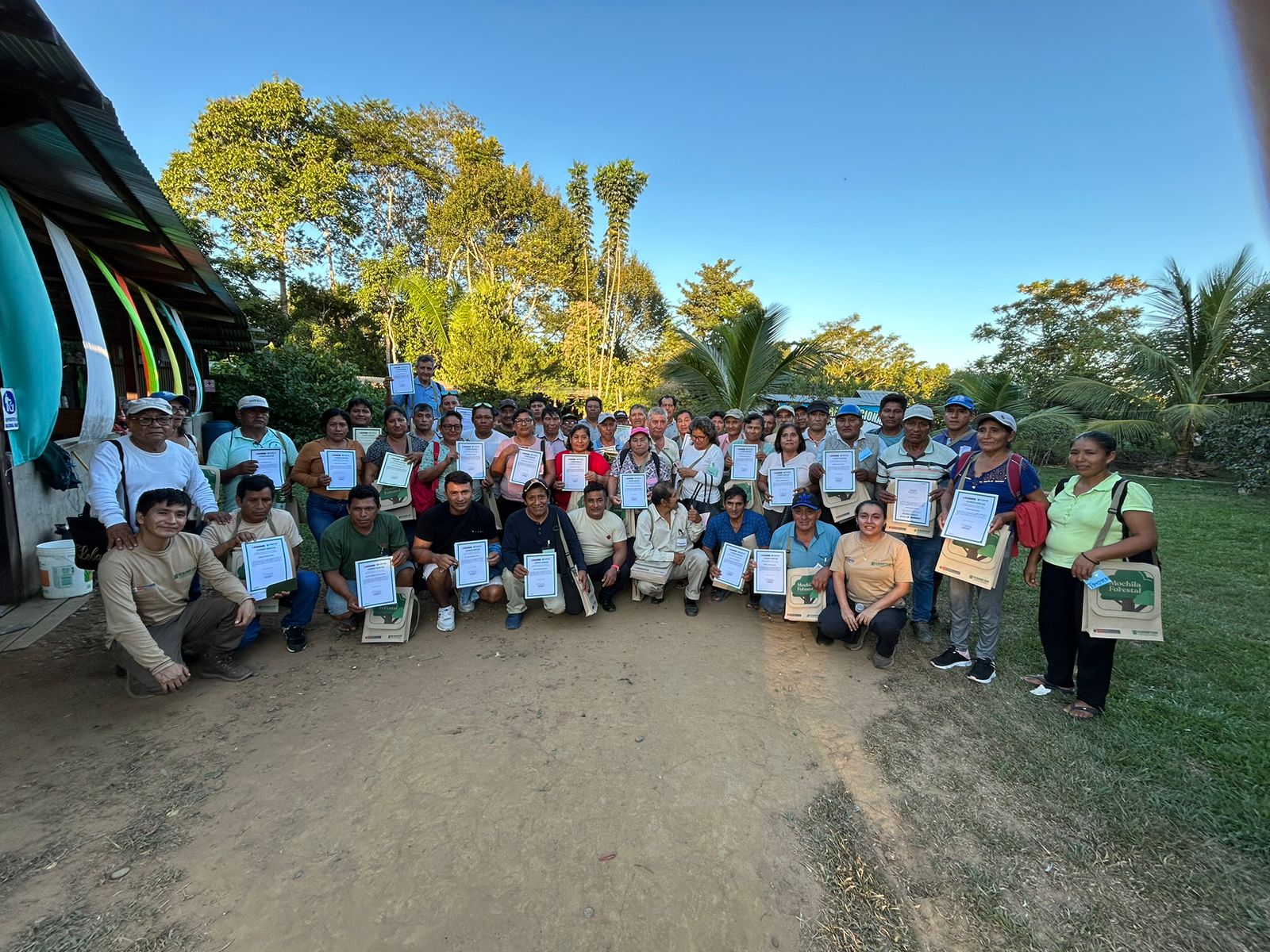
Community engagement is embedded in every activity, ensuring that forest concession holders are not only the beneficiaries but active partners in protection and restoration efforts. This includes training in sustainable harvesting, support for value‑added processing of forest products, and the creation of additional income‑generating opportunities that align with long‑term conservation goals.
Key pillars
The Together for Forests REDD+ Project is founded on a cooperative model that empowers local forest owners to lead conservation from the ground up. Through COOPAFSAMAD, members coordinate forest protection efforts across a vast and varied landscape — from dense lowland rainforest to river systems and wildlife corridors.
Biodiversity conservation is a central pillar: activities preserve and restore habitat for threatened and endangered species, while scientific and community‑based monitoring ensures early detection of threats. Climate action is integrated into every stage, with the project reducing greenhouse gas emissions by avoiding deforestation, restoring degraded land, and sequestering carbon through agroforestry.
Sustainable livelihoods drive long‑term success by aligning conservation with economic benefit; income from certified forest products, agroforestry crops, and ecosystem services enables concession holders to maintain forest cover while supporting their families. Finally, robust governance structures — transparent, participatory, and accountable — ensure fair distribution of benefits and lasting community support.

Cooperative Leadership
Owned and led by local forest concession holders through COOPAFSAMAD, ensuring grassroots governance.
One

Forest Protection
Safeguarding 260,000 ha of Amazon rainforest from illegal logging, mining, and deforestation.

Monitoring & Management
Strengthened governance and new monitoring systems to detect and prevent illegal activity.

Biodiversity Protection
Conserving habitat for jaguars, caimans, tapirs, and the region’s extraordinary bird diversity.
One

Sustainable Livelihoods
Supporting timber and non‑timber forest products, agroforestry, and value‑added processing.

Climate Action
The project’s REDD+ activities reduce emissions, restore degraded land, and maintain a critical carbon sink.
Safeguards
The project applies VERRA Climate, Community & Biodiversity Standards (CCB) to guarantee environmental integrity, social inclusion, and climate benefits. Led directly by forest owners, it ensures that decision‑making, project implementation, and benefit sharing are transparent and equitable.
Safeguard measures include:
1. Participatory governance: Forest owners meet regularly through cooperative structures to set priorities, review progress, and address community needs.
2. Rights andlivelihoods:Benefits from carbon finance and sustainable forestry are distributed among members, improving income security and reducing reliance on destructive activities.
3. Biodiversity safeguards: Activities are designed to protect high‑value species and key habitats while restoring degraded agricultural land to ecological functionality.
4. Transparent accountability: Enhanced institutional capacity within COOPAFSAMAD ensures effective forest management over the long term.




Ready to invest in the future of nature?
Silvania is building a new asset class rooted in nature — mobilising capital into high‑integrity projects that protect biodiversity, strengthen climate resilience, and deliver lasting benefits for communities worldwide.
Whether you are investing for long‑term value, sourcing premium environmental credits for your organisation, or simply wish to learn more, we invite you to start the conversation with us.
